Factors to Consider When Selecting the Right Control Valve
What Are the Basics of Control Valves
The Purpose and Function of Control Valves
Control valves are vital in operations as they control the flow rate and temperature of fluids to ensure efficiency and safety in system conditions. They are used to maintain process conditions by regulating the flow of liquids or gases in various industries, including oil and gas production and power generation.
Common Types of Control Valves
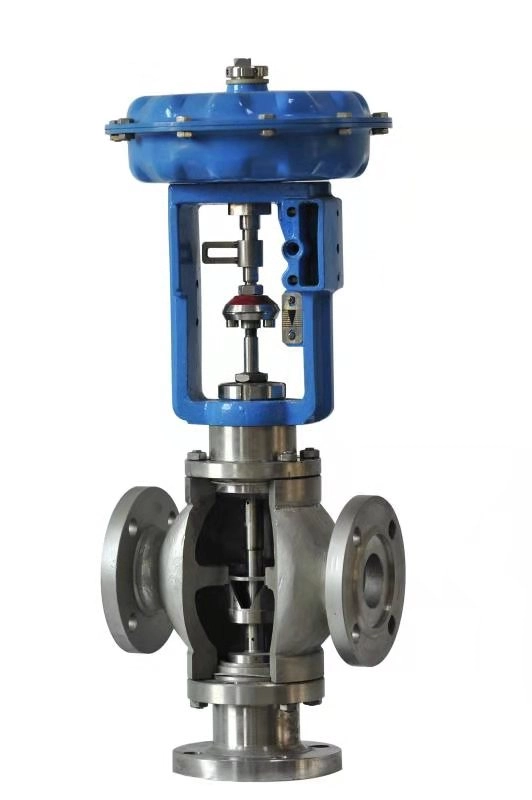
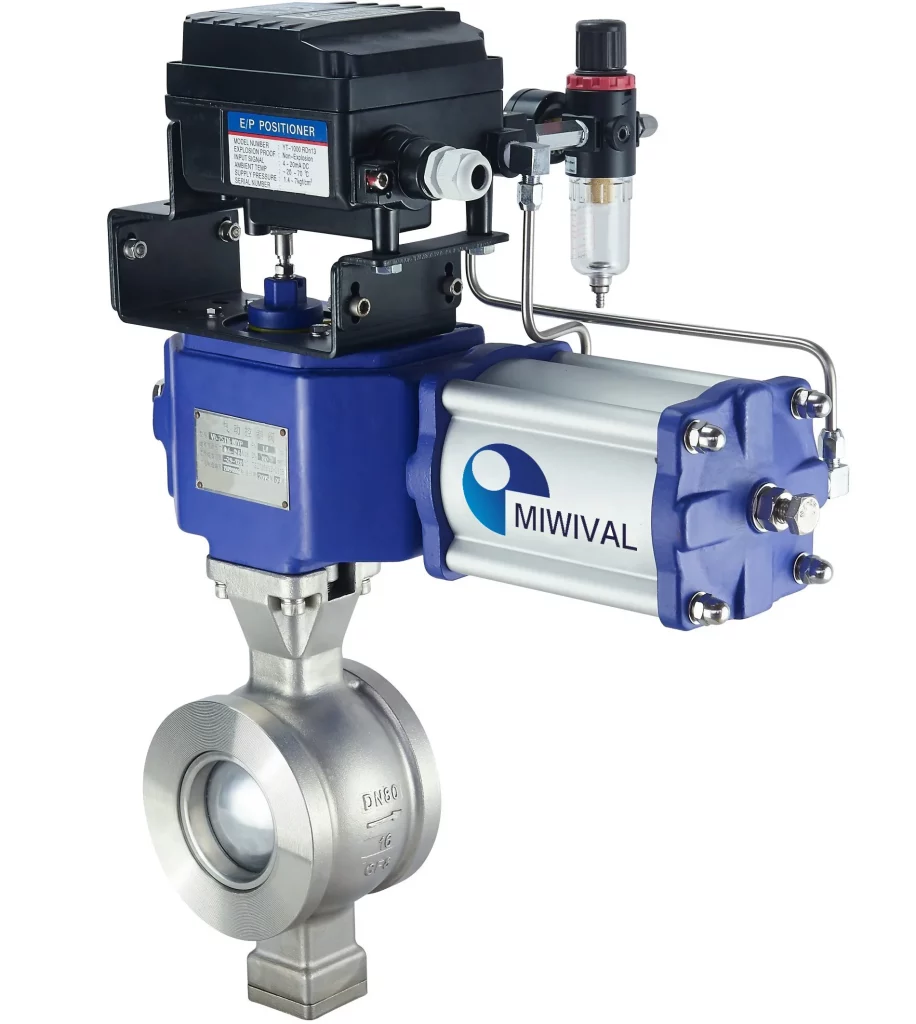
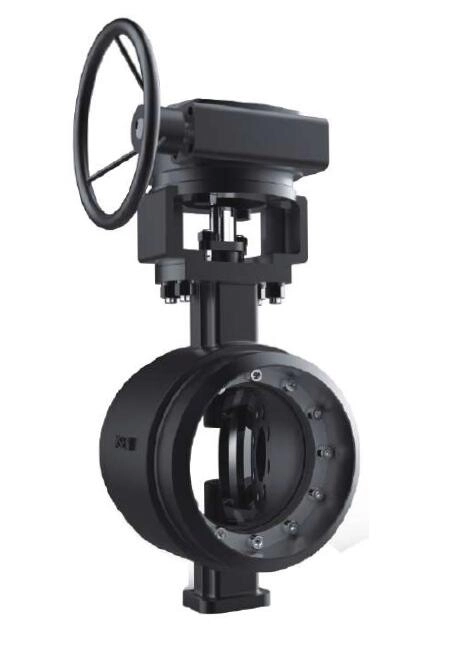
Different types of control valves are used for different purposes; Globe valves are known for their precise control of fluid flow; Ball valves are durable with high flow capacity and ideal for quick shut-off needs; Butterfly valves are cost-effective and can handle large fluid volumes efficiently with minimal pressure loss.
Key Components of a Control Valve
In a control valve setup there are various important parts that collaborate to manage the flow of liquids effectively. The actuator is in charge of adjusting the valve mechanisms according to cues from a control system. The valve body encloses the parts and offers a route for fluid movement. The trim comprises the plug and seat. Stem that directly manages how the fluid flows through the valve. Extra elements like positioners and sensors, boost the valve’s efficiency by guaranteeing positioning and feedback.
What Do You Need for Evaluating Process
Flow Characteristics and Range
When assessing the selection of a control valve for a system or operation it is crucial to grasp the flow properties and scope involved. The valve should manage both the highest flow rates effectively while maintaining precision and consistency. The flow properties indicate how the valve’s aperture corresponds to the flow rate offering linear or equal percentage options based on needs.
Pressure and Temperature Considerations
Pressure and temperature play a role in deciding if a control valve is a good fit for a specific task or not. It is critical that the valve can tolerate pressure and temperatures without deforming or degrading. Additionally, pressure drops throughout the valve should be minimized in a bid to save energy while offering superior performance in applications.
Compatibility with Process Fluids
Materials for the construction of a control valve should be able to match with chemicals it is to control once it is used. In using it with abrasive fluids, materials to use must be stainless steel or special coating in order to avoid wearing down with time. Compatibility also covers seals and gaskets to be compatible with being exposed to chemicals or heat without wearing down.
Selecting the Appropriate Valve Type
Globe Valves for Precision Control
Globe valves are best suited to applications requiring the regulation of levels of fluid flow because of the manner in which they can be accurately adjusted to deliver accurate throttling control—a feature that makes them best suited to processes in which a specific flow rates must be maintained. Globe valves tend to be utilized in systems handling steam, water, and other fluids that require precision, in service.
Ball Valves for High Flow Capacity
Ball valves are utilized best in applications where a need for high flow rate and rapid shut-off is required along with minimum effort. Ball valves are characterized by their design of low-pressure loss and safe performance even under high pressure. Ball valves are utilized best in oil, gas, and heavy fluid pipelines because they have long usage life with low maintenance demand.
Butterfly Valves for Cost-Effective Solutions
Butterfly valves provide a cost option for regulating substantial amounts of fluid within limited installation space requirements while keeping efficiency intact and system costs down overall. They are commonly used in water treatment facilities and HVAC systems among industries that prioritize cost effectiveness without compromising functionality.
Safety and Compliance Considerations
Meeting Industry Standards and Certifications
In choosing a control valve for use It is important to stick to industry standards and ensure the valve meets certifications from such recognized institutions as the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) International Organization for Standardization (ISO) or European Pressure Equipment Directive (PED). These certifications confirm the valve’s reliability and safety in industrial settings by verifying its ability to handle specific pressure and temperature conditions while meeting performance requirements crucial for operational efficiency.
In industries like chemical processing and oil and gas sectors where safety is crucial and hazards are present control valves must meet certain certifications such as ATEX (used in explosive atmospheres equipment ) or SIL (Safety Integrity Level). These certifications evaluate the valve’s performance under challenging conditions to reduce the chances of failure and ensure operations. Maintaining documentation of these standards is essential to comply with regulations and offer reassurance to operators.
Incorporating Safety Features in Valve Design
Control valves nowadays come equipped with safety enhancements to improve their dependability. For instance, safe systems are in place to guarantee that the valve returns to a secure state—either fully open or closed—should there be a power outage or actuator malfunction. This aspect is crucial in situations where unregulated fluid movement might result in outcomes.
Control valves have pressure relief systems installed in them to assist in maintaining safety features operational to avoid any potential harm from the overbuilding of pressure on the equipment and environment through controlled vent release of the fluid whenever required to protect both the machinery and people from harm effectively. Furthermore the application of materials, in making these valves not only extends the lifespan of them but also eliminates the dangers of corrosion or wearing out that might occur after quite some time.
Control valves are designed with features using smart positioners and sensors that monitor performance metrics in real time such as valve position, flow rate, and pressure to predict maintenance needs and detect issues early on. This strategy helps reduce downtime and improve the safety of the system as a whole.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Costs of Control Valves
Ease of Maintenance and Repairability
The cost and efficiency of operating a control valve are greatly influenced by how easy it is to maintain it over time. Valves that have parts make it simple to take them apart and put them back together when maintenance is needed. This design element cuts down on repair time, keeps industrial operations running smoothly with fewer interruptions.
Control valves with built-in self-features make maintenance easier. They offer in-depth information on the condition of components like seals and actuators. Moreover, they let operators know about potential issues such as seal wear and tear or pressure irregularities before these issues become serious problems that could lead to significant breakdowns incidents in the future. By resolving these issues promptly, Facilities can prevent expensive repairs and unexpected shutdown situations.
Manufacturers frequently offer maintenance guides and training sessions to aid technicians in efficiently servicing control valves. Having access to spare parts is also essential as it allows for swift replacements and minimizes downtime when carrying out repairs.
Assessing Long-Term Operational Costs
Energy efficiency and durability significantly influence long-term operational expenses. Efficient valves, such as ball valves with streamlined designs, minimize pressure drops, maintaining flow rates while reducing energy costs. Durable materials like stainless steel or corrosion-resistant alloys extend service life in harsh conditions, lowering replacement frequency and lifecycle costs.
Actuator selection and maintenance strategies further impact costs. While pneumatic actuators have lower upfront costs, electric actuators offer energy efficiency and reduced maintenance. Regular inspections prevent unexpected failures, avoiding costly downtime. High-quality valves with advanced features despite higher initial investment, yield savings through prolonged lifespan and minimized upkeep.
Efficient valves, such as the ones Miwival offers with ball valves featuring streamlined designs, minimize pressure drops, maintaining flow rates while reducing energy costs. The company’s valves are crafted with a focus on energy – saving technologies, ensuring that users can achieve substantial savings on their long – term energy bills.
FAQ
Q: What flow characteristics should be evaluated?
A: Match valve trim (e.g., linear, equal percentage, or quick-opening) to the system’s flow requirements. For example:
Linear trim for proportional control in process industries.
Equal percentage trim for systems requiring gradual flow adjustment.
Q: How important are maintenance and service life in selection?
A: Opt for valves with accessible components for easy maintenance. Features like replaceable seats or modular designs reduce downtime. Valves with self-diagnostic capabilities (e.g., smart valves with IoT integration) enhance predictive maintenance.